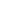Về dB, dBm và dBi
Ước tính 15 phút để đọc xong
D B (decibel)
DB là đơn vị tương đối dùng để biểu thị tỷ lệ giữa hai đại lượng. Nó thường được sử dụng để mô tả tỷ lệ công suất hoặc điện áp (hoặc dòng điện).
Định nghĩa: (dB=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P_2} {P_1} \ right)) hoặc (dB=20 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {V_2} {V_1} \ right) )
Trong số đó, (P_1) và (P_2) là hai giá trị công suất và (V_1) và (V_2) là hai giá trị điện áp hoặc dòng điện.
Lưu ý: dB là đơn vị tương đối biểu thị tỷ số giữa hai đại lượng, không phải giá trị tuyệt đối.
1. Công thức tính decibel tỉ số công suất:
Khi so sánh hai giá trị công suất, công thức tính decibel là:
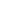
DB=10log10 (P1P2), trong đó (P_1) là công suất tham chiếu (thường là giá trị cố định) và (P_2) là công suất cần đo. Nếu (P_1) là 1 watt thì công thức trên có thể được đơn giản hóa thành: dB=10log10 (P2), trong đó (P_2) là giá trị công suất tính bằng watt.
2. Công thức tính decibel tỷ số điện áp (hoặc dòng điện):
Khi so sánh hai giá trị điện áp (hoặc dòng điện), công thức tính decibel là:
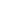
dB=20log10(V1V2)
có lẽ
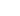
dB=20log10(I1I2)
Trong số đó, (V_1) và (I_1) là điện áp và dòng điện tham chiếu (thường là giá trị cố định), trong khi (V_2) và (I_2) là điện áp và dòng điện cần đo. Nếu (V_1) hoặc (I_1) là 1 volt hoặc 1 ampe, công thức trên có thể được đơn giản hóa như sau:
dB=20log10(V2)
có lẽ
dB=20log10(I2)
Here (V_2) and (I_2) are voltage and current values in volts or amperes.
Note: In these formulas, (\ log_ {10}) represents the logarithm based on 10. If (P_2/P_1) or (V_2/V_1) (or (I_2/I_1)) is greater than 1, then the decibel value is positive; If it is less than 1, the decibel value is negative. The larger the decibel value, the greater the multiple of (P_2) relative to (P_1) (or (V_2) relative to (V_1), or (I_2) relative to (I_1)).

DBm (decibels milliwatts)
DBm is an absolute unit used to represent power values, with a reference point of 1 milliwatt (0.001 watt).
Definition: (dBm=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P} {1mW} \ right))
Where (P) is the power value to be measured.
For example, if the power of a signal is 1 watt, then its power is (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30 dBm).
DBm is commonly used to describe the power of wireless signals or the sensitivity of receivers.
DBm calculation formula
dBm=10log10(1mWP)
Among them,
(P) is the power value to be measured, in milliwatts (mW).
(1mW) is the reference power value, which corresponds to the power of 0dBm.
Related information
1. Unit conversion:
0dBm corresponds to 1 milliwatt (1mW).
For every 3dBm increase, the power doubles; For every reduction of 3dBm, the power is halved.
For example, 30dBm corresponds to 1 watt (1W), because (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30) (because 1W=1000mW).
2. Common conversion values:
o 30dBm = 1W
o 40dBm = 10W
o 50dBm = 100W
3. Precautions:
DBm represents the absolute value of power, not the power ratio.
In the calculation, pay attention to the unit of power and ensure that it is consistent with the unit of reference power (1mW).
Example
If the power of a signal is 4 watts (4W), then its power (in dBm) can be calculated as follows:
dBm=10log10(1mW4000mW)=10log10(4000)=10*(3+log10(4))≈36.02dBm
(Here (\ log_ {10} (4) \ approx 0.602) is the base 10 logarithm of 4)
DBi (decibels relative to isotropy)
DBi is a unit used to describe antenna gain, with its reference point being an idealized isotropic antenna (i.e. an antenna that uniformly radiates or receives in all directions).
Definition: (dBi=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {G} {G_ {iso}} \ right))
Among them, (G) is the gain of the antenna to be measured, and (G_ {iso}) is the gain of an isotropic antenna (theoretically 1).
Note that since isotropic antennas do not exist in reality, dBi is a relative unit, but it provides a convenient reference point to compare the gains of different antennas.
DBi is commonly used to describe the gain of antennas used in wireless communication.
DBi calculation formula
dBi=10log10(E0E)
Among them:
(E) is the effective radiation power or gain of the actual antenna.
(E0) is the effective radiation power or gain of an ideal isotropic antenna. An ideal omnidirectional antenna has uniform radiation in all directions, and there is no such antenna in practice, so it serves as a reference benchmark.
Related information
1. Điểm chuẩn tham chiếu: Điểm chuẩn tham chiếu cho dBi là ăng-ten đa hướng, là mô hình lý tưởng về mặt lý thuyết được sử dụng để so sánh mức tăng của các ăng-ten khác.
2. Mối quan hệ với dBd: dBi và dBd đều là đơn vị mô tả mức tăng ích của anten, nhưng tiêu chuẩn tham chiếu của chúng là khác nhau. Điểm chuẩn tham chiếu cho dBi là ăng-ten đa hướng, trong khi điểm chuẩn tham chiếu cho dBd là ăng-ten lưỡng cực
(Anten lưỡng cực). Người ta thường tin rằng khi biểu thị cùng một mức tăng, giá trị được biểu thị bằng dBi lớn hơn 2,15 so với giá trị được biểu thị bằng dBd (tức là dBi=dBd+2,15).
3. Ví dụ: Nếu mức tăng ích của ăng-ten được biểu thị bằng 16dBd tính bằng dBd thì mức tăng ích của nó được biểu thị bằng 18,15dBi tính bằng dBi (thường bỏ qua số thập phân mà là 18dBi).
Tóm lại, dBi là đơn vị dùng để mô tả mức tăng ích của ăng-ten và công thức tính toán của nó dựa trên tỷ lệ giữa công suất bức xạ hiệu dụng của ăng-ten thực tế và công suất bức xạ hiệu dụng của ăng -ten đa hướng lý tưởng . So với dBd, dBi quy chiếu là anten đa hướng nên khi biểu diễn cùng một mức tăng ích thì giá trị dBi sẽ lớn hơn giá trị dBd 2,15.

















 Mimo .ăng ten.
Mimo .ăng ten.